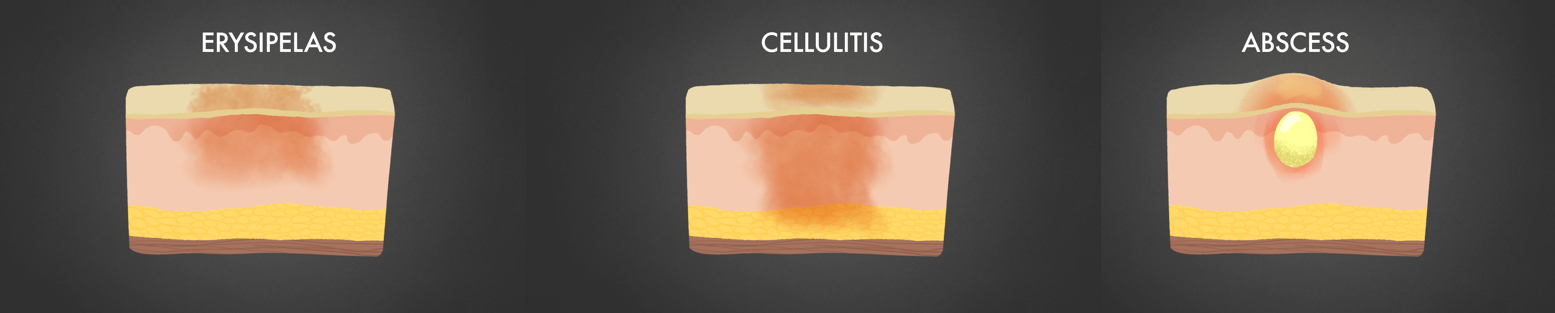
Soft Tissue & Bone Infections
Case 4:
Mr. Skywalker is a 46 year old man who had traumatic amputation of his right hand approximately 20 years ago and has had repeat surgeries with prostheses placement to his right upper extremity since. He currently has a prosthetic hand (made of a metallic substance you are unfamiliar with) that was inserted one month ago at an outside hospital. He presents to the ED with progressive, dull pain at his wrist adjacent to the prosthesis, and some adjacent erythema. He reports that these symptoms have been present for 2 weeks and have not improved with oral antibiotics. His vital signs are stable. MRI (fortunately, his metalloid hand was MRI-compatible) reveals bone marrow edema of the right distal radius adjacent to his prosthesis, suggestive of osteomyelitis. Which of the following is the next best step?
a. Collect blood cultures and then start empiric vancomycin and ceftriaxone.
b. Collect blood cultures and then start vancomycin and pip-tazo to cover hospital-acquired pathogens given his recent surgery.
c. Collect blood cultures and page Orthopedics to evaluate the extremity and obtain deep wound or bone culture if possible.
d. Collect blood cultures and page IR for bone biopsy and culture.
Explanation:
Blood cultures should be collected in all suspected cases of osteomyelitis. This case is an example of hardware-associated osteomyelitis and so surgical evaluation is needed (often, hardware needs to be removed for adequate source control). The correct answer is C. Remember, always try and get a deep wound or bone culture PRIOR to starting antibiotics; these patients are usually not septic!